Appendix A – Forms
Apprenticeship Instructor Approval Letter
CCP Registered Apprenticeship Program
Instructor Credentialing Statement
To: Academic Deans’ Council
Re: Instructor ________________________
Registered Apprenticeship Program: ____________________
Date: ____________
This instructor has met the Registered Apprenticeship Program Standards of Journeyman as defined by Section 446.021(4) Florida State Statute, which states “a person working in an apprenticeable occupation who has successfully completed a registered apprenticeship program, or who has worked the number of years required by established industry practices for the particular trade of the occupation.”
The instructor has been screened and qualifies (approved) by the Registered Apprenticeship Program Committee to teach all levels of registered apprenticeship classes both on-the-job training (OJT) and related instruction necessary for program completion.
Authorized by: _________________________________________________
Committee Chairperson, Registered Apprenticeship Program
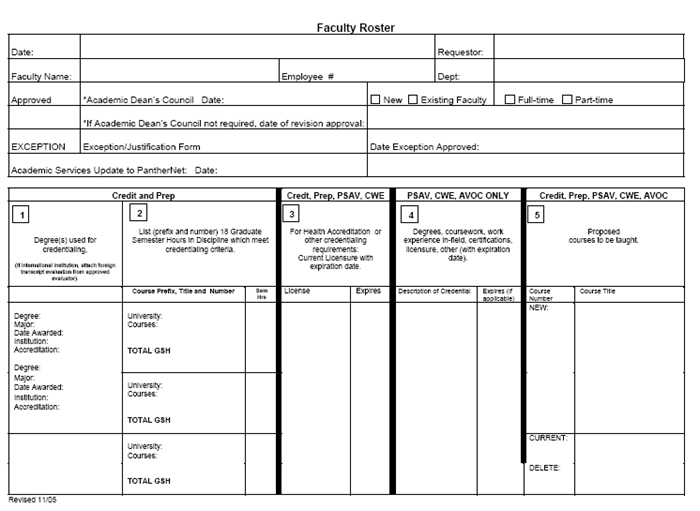
Faculty Roster Form
(for review of full-time faculty candidates prior to interview)
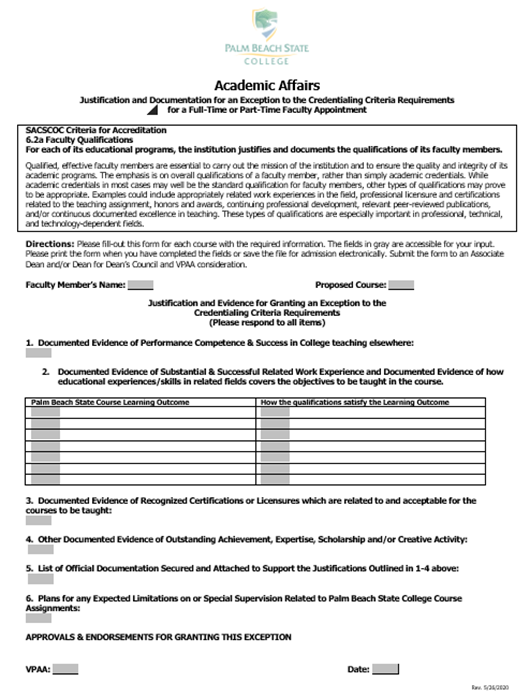
Justification for Exception to Credentialing Criteria Form
Print Form
Appendix B - Mathematics Courses – Nova Southeastern University
The following courses are approved to satisfy the 18 GSH for teaching mathematics.
MAT 505 Geometry for Mathematics Teachers (3 Cr)
This course is designed to offer a wide perspective on geometry for graduate students planning to teach secondary mathematics. The course covers both Euclidean and non-Euclidean geometry.
MAT 507 or MAT 681 Linear and Abstract Algebra (3 Cr)
This course provides theory and computational practice with Linear Algebra, as well as a theoretical foundation for Abstract Algebra structures such as rings, fields, and groups. Students will create two portfolios of notes, activities, and exercises: one for Abstract Algebra, and one for Linear Algebra. Prerequisite/s: College Algebra and MAT 0503.
MAT 514 Topics in Algebra and Geometry (3 Cr)
This course covers concepts in number theory, the real number system as well as algebra and geometry. The emphasis is on algebraic models (linear, quadratic, and exponential) and their applications. Additionally, this course will serve students well as a foundation course leading to further study in more advanced topics in algebra, geometry, trigonometry and calculus.
MAT 515 Probability and Statistics (3 Cr)
This course is designed to give students an introduction to probability and statistics with a focus on problem solving. The course includes set theory, Venn diagrams, combinations and permutations, probability, and expected value and concludes with a unit in descriptive statistics and normal distributions. A class project requires students to think critically as well as apply the concepts learning in the course.
MAT 516 Elements of Differential Calculus (3 Cr)
Topics include Limits, Continuity, Definition of the Derivative, Rules of Differentiation, Implicit Differentiation, Applications of the Derivative; Curve Sketching, Related Rates, and Optimization problems.
MAT 517 Elements of Integral Calculus (3 Cr)
The second part of the two-course calculus sequence MAT516/MAT517. Topics include differentiation and applications of exponential and logarithmic functions, indefinite integrals via the anti-derivatives, definite integrals, calculating area using Riemann sums and the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, properties of the definite integral, integration by substitution, integration by parts, use of integration tables, additional applications of the definite integral to probability theory, volumes of revolution, and separations of variables.
MAT 591 Calculus for Teachers I (3 Cr)
This course is a proof-based "epsilon-delta" calculus, ranging from limits and cluster points to differentiation. Students will solve standard calculus problems computationally and theoretically. Students in this course should have completed College Algebra and Trigonometry, or equivalent courses. Prerequisite/s: MAT 0503
MAT 592 Calculus for Teachers II (3 Cr)
This course is a proof-based "epsilon-delta" calculus, ranging from integral calculus to sequences and series, and cluster points to differentiation. Students will solve standard calculus problems computationally and theoretically. Students in this course should have completed Calculus I or an equivalent course. Prerequisite/s: MAT 0592.
MAT 685 Symbolic Representation and Number Theory in Mathematics (3 Cr)
This course will focus on notational systems, number theory, and the rationale behind them. The increasing use of manipulative and kinesthetic learning will also be addressed. This course is designed to include significant number theory preparation for students wishing to earn initial certification. Prerequisite/s: College algebra and MAT 0503.
MAT 689 Probability and Statistics in Mathematics Education (3 Cr)
This course offers preparation in probability and statistics for the secondary mathematics teacher, as well as for teachers pursuing their initial teacher certification. Also, students will gather and analyze statistics in educational research.
Appendix C - Guidelines for Credentialing Science Faculty
The following guidelines represent discipline areas for examining transcripts of applicants in selected courses as noted below.
All of the courses should be at the graduate level.
BSC 1005/L:
Possible discipline areas on the transcript: Zoology, Botany, Microbiology, Genetics, Cell Biology, Molecular Biology.
BSC 1010/L:
Possible discipline areas on the transcript: Zoology, Botany, Microbiology, Genetics, Biochemistry, Cell Biology, and Evolution.
BSC 1011/L:
Possible discipline areas on the transcript: Zoology, Botany, Microbiology, Genetics, Cell Biology, Molecular Biology, Vertebrate Zoology or Comparative Anatomy, Invertebrate Zoology.
ZOO 2303:
Possible discipline areas on the transcript: Zoology, Botany, Microbiology, Genetics, Cell Biology, Molecular Biology, Ichthyology, Ornithology, Mammalogy, or Herpetology.
BSC 2085/L, BSC 2086/L:
Possible discipline areas on the transcript: Comparative Anatomy or Vertebrate Zoology, Animal Physiology and Biochemistry, plus at least two of the following, Human Embryology, Neurobiology, Endocrinology, Cytology or Cell Biology, Histology, or Cell Physiology, Cancer Biology.
MCB 2010/L:
Possible discipline areas on the transcript: Immunology, Parasitology, Bacteriology, Medical Bacteriology, Virology, Advanced Virology, Endocrinology, Cytology, Ultra-structure.
BSC 1050/L:
Possible discipline areas on the transcript: Zoology, Botany, Microbiology, Genetics, and at least one graduate level class in Ecology.
Appendix D - Position Statement from HAPS on Human Anatomy and Physiology Society

Approved November 19, 2005
Position Statement on Accreditation of Faculty in 2-semester Human Anatomy and Physiology Courses
HAPS • 8816 Manchester, Suite 314 • St. Louis, MO 63105
1-800-448-4277 • www.hapsweb.org
Background:
The 2-semester/3-quarter undergraduate course usually known as "Human Anatomy and Physiology" or simply "Anatomy and Physiology" is a large introductory course that may be offered by the Biology, Zoology, or Natural Sciences departments. Nationwide, roughly two-thirds of these courses are taught at community colleges, and the rest primarily at universities. This is one of the larger introductory level courses, with approximately 450,000 students enrolled each year in the US and Canada.
The majority of students taking the 2-semester A&P course are planning a career in the health sciences. The career paths include nursing, occupational therapy, physical therapy, radiation technology, laboratory/medical technology, dental hygiene, pharmacology and other related disciplines. Students majoring in physical education, sports training, or kinesiology make up a smaller component of the classroom population. At community colleges the course is often taken in the first year of college, without college-level prerequisites. Entry into any one of the career programs listed above is contingent upon successful completion of the A&P course with a grade of ‘C’ or above; in competitive programs, the grade requirements may be much more restrictive.
It is important to note that pre-medical students and biology majors do not typically take this course because it is an option that does not count towards their degree requirements. Instead, they will take Majors Biology (or Zoology/Botany) as freshmen, followed by more specialized and detailed upper level courses in their junior and senior years. However, the distinction between biology majors and allied health majors is an administrative convenience and not an indication that A&P is anything other than an integrative biological science.
Anatomy and Physiology as a Biological Science
As an introductory level survey course, A&P covers a diversity of topics, including not only anatomy and physiology, but introductory biochemistry, cytology, histology, molecular biology, genetics, immunology, nutrition, embryology, and pathology. The coverage is so diverse, and the principles so relevant to a general understanding of modern biology, that a 1-semester version of this course is often used to satisfy the general biology requirements for non-major students.
Two-semester A&P courses are usually taught from the Biology, Zoology, or Natural Sciences departments; in rare cases, the sequence may be offered by another academic division (e.g. a department within an associated medical school) as a service course. As a result, the diversity of faculty roughly approaches the diversity of topics presented within the course.
The Need for Standardization of Criteria for the Selection and Accreditation of Faculty:
Faculty qualification standards that are too lax make it difficult for the assigned faculty to teach the core curriculum topics, whereas standards that are too restrictive negatively impact both faculty and students. It is in the best interests of all parties to use a standardized set of criteria when evaluating the faculty of anatomy and physiology courses during an accreditation review. For example, at one college the application of overly restrictive standards, which refused to accept comparative, vertebrate, mammalian, or clinical courses among the relevant course credits required for faculty qualification, led to the dismissal of faculty and the elimination of associated A&P and Microbiology courses from the curriculum.
It is our position that Human Anatomy and Physiology is a subset of biology, and the course has extensive overlap with other biological sciences. Opportunities to obtain an M.S. or Ph.D. degree in “human anatomy and physiology” are extremely limited, but there is so much duplication of coverage among courses in modern biology that such specialization is unnecessary. Because the basic anatomical, physiological, histological, and developmental patterns are found across the vertebrate lineage (and often across the major animal phyla), a great diversity of biology courses are directly applicable to human A&P. We also believe that any evaluation of current or potential instructors should consider graduate and postgraduate teaching experience in courses related to anatomy and physiology toward satisfaction of minimum criteria.
HAPS has developed accreditation standards based on a survey of successful anatomy and physiology courses nationwide. We feel that these criteria are sufficient to demonstrate that an instructor is competent to teach a 2-semester anatomy and physiology course. We are therefore encouraging all accreditation agencies and college administrations to use these criteria when evaluating courses or prospective faculty.
The HAPS Standards for Instructors in Anatomy and Physiology:
The HAPS minimum criteria for teaching the introductory level A&P course are (1) a Master’s degree in one of the biological sciences and (2) 18 related credit hours as defined below. A professional degree (M.S.N., M.D., D.O., D.C. D.V.M., or other advanced clinical degrees awarded by nationally accredited institutions) may be accepted as fulfilling the degree requirements.
Instructors must be prepared to integrate introductory level chemistry and biochemistry not only with anatomy and physiology, but with a variety of other relevant topics in biology, including cytology, cell physiology, histology, organology, microbiology, immunology, embryology, and nutrition. Because of the interrelatedness of topics in biology, a course in any one of the topics above must of necessity include a significant amount of anatomy and physiology. Using the HAPS Curriculum Guidelines as a reference, Attachment 1 lists courses that are relevant to the teaching of anatomy and physiology at the introductory level. This list is intended as a reference and a guide, not as a comprehensive or exclusionary listing of applicable courses.
The 18 related credit hours can be accumulated through a combination of (1) undergraduate and graduate course work, (2) teaching experience as a graduate teaching assistant or as graduate or postgraduate faculty in A&P courses, (3) postgraduate course work in human anatomy and physiology, including continuing education credits, (4) research in the field of A&P as evidenced by publication in peer-reviewed journals.
Credits should be calculated as follows:
- for coursework: the credits awarded on the relevant student transcripts or continuing education certificate
- for graduate TA work or as faculty while a graduate student: the credits awarded on the graduate student transcript or the credit value of the course
- for postgraduate teaching: 3 credits for each semester taught
- for continuing education: the CE credits or units awarded for satisfactory completion of coursework in human anatomy and/or physiology
- for research publications: 3 credits for each peer-reviewed journal article
- Any questions regarding this position statement should be directed to the HAPS President and the Board of Directors. A current copy of the Course and Curriculum Guidelines may be downloaded from the HAPS website at http://www.hapsweb.org.
Courses relevant to the teaching of human anatomy and physiology*
Anatomy-related:
- Human anatomy
- Comparative anatomy
- Vertebrate anatomy
- Veterinary anatomy
- Surgical anatomy
- Gross anatomy
- Neuroanatomy
- Physical anthropology
- Kinesiology
- Human embryology
- Comparative embryology
- Vertebrate embryology
- Cytology
- Histology
- Organology
- Pathology
Physiology-related:
- Human physiology
- Animal physiology
- Comparative physiology
- Mammalian physiology
- General physiology
- Medical physiology
- Veterinary physiology
- Pathophysiology
- System physiology (i.e., neurophysiology, cardiovascular physiology, endocrinology, immunology, respiratory physiology, etc.)
- Cell physiology
- Exercise physiology
- Molecular biology
- Genetics
- Ancillary courses of value**:
- Microbiology
- Nutrition
- Biochemistry
- Pharmacology
- Pharmacophysiology
*Note: This list should not be considered comprehensive. It is meant simply to provide an indication of the diversity of topics directly relevant to human anatomy and physiology, as reflected in the HAPS Core Curriculum Guidelines.
**A maximum of 6 credits from this category ay be counted toward the 18-credit requirement.
Appendix E - Acceptable Mathematics Courses from Florida Atlantic University’s Master’s Degree in Teaching Mathematics
Note: All Special Topic courses (typically with the number MXX 693X) to be considered for credentialing must provide the course description. These courses are not included on the list below.
| Course Number |
Course Title and Description |
| MAS 6271 |
Number Theory and Cryptography (3 credits)
Elementary number theory with applications to cryptography, including: congruences and modular arithmetic, finite fields, public key cryptography (RSA), primality testing and factoring. |
| MAS 6318 |
Advanced Algebra and Geometry (3 credits)
Prerequisites: MAS 2103 and MAS 4301
Integrative treatment of advanced topics in classical algebra and geometry. Not intended for students in the Ph.D. program in mathematics. |
| MAT 6516 |
Problem Solving and Recreational Mathematics (3 credits)
Prerequisites: MAA 4200 and MAS 4301
Introduction to mathematical problem-solving literature, principles and methods of problem solving, and analysis of selected famous problems in recreational mathematics. Not intended for students in the Ph.D. program in mathematics. |
| MTG 6415 |
Fractal Geometry (3 credits)
Prerequisite: Permission of instructor
Fractal geometry describes the seemingly irregular shapes and patterns we encounter in the natural world. This course explores the mathematical concepts behind fractal geometry and gives numerous applications of integration of mathematics with the natural world. |
| MTG 6226 |
Advanced Euclidean Geometry (3 credits)
Prerequisites: MAS 2103 and MAS 4301
Emphasizes the uses of homogeneous barycentric coordinates in triangle geometry and of dynamic software to explore basic theorems and problems. Not intended for students in the Ph.D. program in mathematics. |
| MTG 6418 |
Dynamical Systems, Chaos, and Computing (3 credits)
Prerequisite: Permission of instructor
Students reconstruct some modern mathematical discoveries in dynamical systems using widely accessible programs such as spreadsheets and dynamical geometry software. Explorations illustrate the relation of chaos theory to iteration of second order polynomials and fractal geometry as well as general mathematical patterns. |
| MHF6410 |
Calculus from a Historical Perspective (3 credits)
Selected topics in calculus from the historical point of view including Archimedes’ quadrature of the parabola, the calculation of Pi, the Bernoulli numbers, and sums of powers of numbers. |
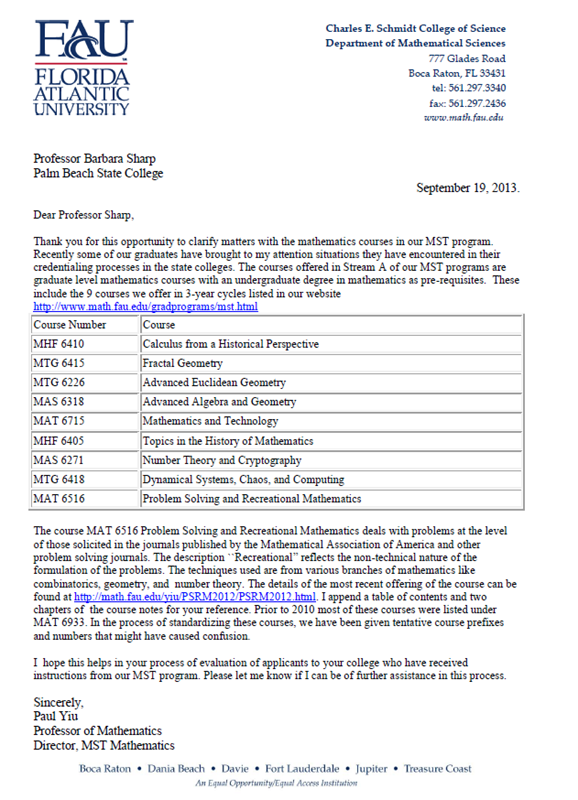
Supplemental Letter from FAU’s MST Program Director
Appendix F - Office of International Education Forms and Documentation
Appendix G - List of Reviewers by Discipline
| DISCIPLINES |
REVIEWER |
| Accounting |
Tracey, Juliett |
| Air Conditioning/HVAC |
Marquez Veray, Eligio |
| Anthropology |
Marx, Luli |
| Apprenticeship |
Marquez Veray, Eligio |
| Archaeology |
Martinez-White, Susy |
| Architecture |
Stukes, Karine |
| Art |
Bierster, Susan |
| Astronomy |
Ridener, Barbara |
| Automotive Maintenance and Light Repair Technician |
Marquez Veray, Eligio |
| Automotive Repair Technician |
Marquez Veray, Eligio |
| Automotive Service Technician |
Marquez Veray, Eligio |
| Automation |
O'Dea, Bob |
| Banking |
Tracey, Juliett |
| Barbering |
Alexander, Andreas |
| Biology |
Mercer, Becky |
| Biotechnology |
Mercer, Becky |
| Biotechnology Lab Specialist |
Mercer, Becky |
| Business Administration & Management |
Tracey, Juliett |
| Business Entrepreneurship |
Tracey, Juliett |
| Chemistry |
Ridener, Barbara |
| Community-Based Learning |
Bierster, Susan |
| Computer Information Systems |
Pentzke, Luis |
| Cosmetology/Facials/Nails |
Marquez Veray, Eligio |
| Crime Scene Technology |
Dixon, Germany |
| Criminal Justice Institute |
Dixon, Germany |
| Criminal Justice Transfer |
Dixon, Germany |
| Dental Hygiene/Dental Assisting |
Mouradian, Belinda |
| Diesel Maintenance Technician |
Marquez Veray, Eligio |
| Early Childhood Education/Entry-Level/Certificate Programs |
Martinez-White, Susy |
| Economics |
Marx, Luli |
| Education |
Martinez-White, Susy |
| Electrical Power Technology |
O'Dea, Bob |
| Electrician |
Marquez Veray, Eligio |
| Emergency Management |
Dixon, Germany |
| Emergency Medical Services/Paramedic/EMT |
Dixon, Germany |
| Engineering |
O'Dea, Bob |
| Engineering Technology |
O'Dea, Bob |
| English/English Preparatory (Developmental Education) |
Keen, Destiny |
| English for Academic Purposes |
Keen, Destiny |
| Environmental Science Technology |
Mercer, Becky |
| EPI- Educator Preparation Institute |
White-Martinez, Susy |
| Fire Science Technology/Fire Recruit |
Dixon, Germany |
| Foreign Language |
Pena, David |
| Geography |
Martinez-White, Susy |
| Geology |
Ridener, Barbara |
| Graphic Design Technology |
Bierster, Susan |
| Health/Health & Fitness/Physical Education |
Mouradian, Belinda |
| Heavy Equipment Service Technician |
Alexander, Andreas |
| History |
Marx, Luli |
| Hospitality Management |
Marquez Veray, Eligio |
| Human Services |
Martinez-White, Susy |
| Insurance |
Tracey, Juliett |
| Interdisciplinary/Honors |
Sheila Scott-Lubin / Sivigny, Julie |
| Interior Design |
Bierster, Susan |
| Journalism/Mass Communications |
Bierster, Susan |
| Landscape & Horticulture Management |
Mercer, Becky |
| Library Science |
Krull, Rob |
| Machining Technology |
Marquez Veray, Eligio |
| Massage Therapy |
Mouradian, Belinda |
| Mathematics/Mathematics (Developmental Education) |
Hamadeh, Dana |
| Medical Assisting (Advanced) |
Mouradian, Belinda |
| Medical Imaging (BS) |
Mouradian, Belinda |
| Mechatronics |
Mercer, Becky |
| Motion Picture, Television Production, Digital Animation and Recording Arts |
Bierster, Susan |
| Music |
Bierster, Susan |
| Nursing (AS) |
Clarke, Carol |
| Nutrition |
Mouradian, Belinda |
| Oceanography |
Ridener, Barbara |
| Office Management Technology |
Tracey, Juliett |
| Office Occupations |
Tracey, Juliett |
| Ophthalmic Medical Technology |
Mercer, Becky |
| Paralegal |
Pena, David |
| Patient Care Assistant |
Clarke, Carol |
| Philosophy |
Marx, Luli |
| Photography |
Stukes, Karine |
| Physical Science |
Ridener, Barbara |
| Physics |
Ridener, Barbara |
| Political Science |
Marx, Luli |
| Practical Nursing |
Clarke, Carol |
| Psychology |
Martinez-White, Susy |
| Public Safety Telecommunications |
Dixon, Germany |
| Radiography |
Mouradian, Belinda |
| Reading (Developmental Education) |
Keen, Destiny |
| Real Estate |
Tracey, Juliett |
| Religion |
Marx, Luli |
| Respiratory Care |
Mouradian, Belinda |
| Security and Automation Systems Technology |
Marquez Veray, Eligio |
| Sociology |
Martinez-White, Susy |
| Sonography |
Mouradian, Belinda |
| Speech |
Pena, David |
| Student Development-Strategies/Leadership |
Keen, Destiny |
| Supply Chain Management |
Tracey, Juliett |
| Surgical Services |
Mouradian, Belinda |
| Surgical Technology |
Mouradian, Belinda |
| Theater |
Bierster, Susan |
| Vocational Preparatory Instruction |
Johnson, Jennifer |
| Welding Technology |
Marquez Veray, Eligio |
| Bachelor’s Degrees |
|
| Entrepreneurship |
Hadley, John |
| Cardiopulmonary Sciences |
Mouradian, Belinda |
| Health Management |
Hang-Fu, Lee |
| Human Services |
Hadley, John |
| Information Management |
Hadley, John |
| Nursing |
Clarke, Carol |
| Project Management |
Hadley, John |
| Supervision & Management |
Hadley, John / Credentialing Process Committee |
Created July 2019, Revised September 2020, Revised June 2021, July 2022, July 2023, July 2024, July 2025